EVSE Standards and Communications
Summary for Decision Makers
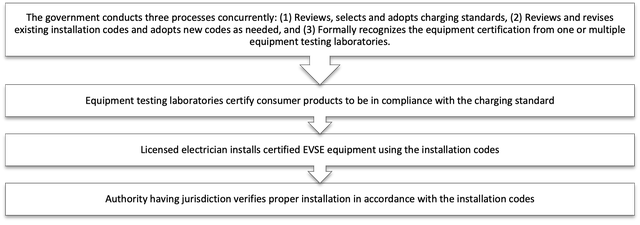
Establishing a regulatory framework of charging standards, equipment certification, and building codes creates a consistent, reliable, and safe operating environment for EVs
Increasingly advanced EV and EVSE technologies are entering the market at a rapid pace. Due to the highly interrelated nature of EV charging technology, it is important to establish a consistent regulatory framework. An effective means of doing this is for policy makers to adopt and enforce internationally or nationally appropriate EV and EVSE codes and standards. This ensures interoperability between different types of EVs and EVSE and establishes a safe and reliable operating environment for consumers and installers. Government selection, adoption, and enforcement of codes and standards can provide consumers with confidence in the long-term viability of EV charging technologies. This in turn may increase investment in these technologies and lower the risk of them becoming prematurely obsolete soon. These efforts support the development of a robust network of charging infrastructure that underpin successful EVSE deployment and increased EV adoption.
What is a regulatory framework?
A regulatory framework governs the connection from:
- The EV to EVSE
- The EVSE to the grid.
Generally, the connection from the EV to the EVSE is governed by charging standards, and the connection between the EVSE to the grid is governed by installation codes.

Policymakers play a pivotal role in supporting this framework by selecting and adopting charging standards that are appropriate for their region, formally recognizing equipment testing laboratories that consumers can trust to verify the safety of new technology and adopting or updating installation codes to remove barriers to EVSE installations. Wherever possible, the regulatory framework should be enforced to ensure compliance. The following figure provides an example of how different entities may enforce compliance at each stage of the regulatory framework.
Codes and Standards
Reviewing current codes and standards will help policymakers understand whether they serve to help or hinder EVSE deployment and adoption
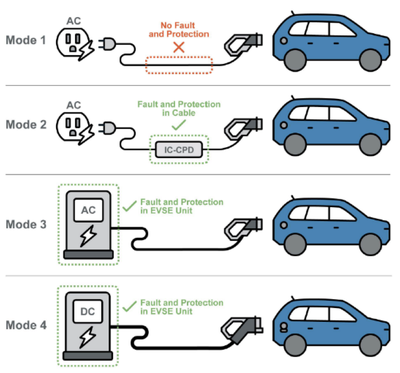
It is important for policymakers to conduct a thorough review of their existing regulatory framework before making changes or additions. Special consideration should be given to reviewing the requirements relating to electrical infrastructure, building design, and construction to examine whether they can currently accommodate safe EVSE installations as existing codes may unintentionally prevent or deter EVSE installations. Once reviewed, codes can be modified or adopted to account for current and future advances in technology. When considering which charging standard to adopt, policymakers should review which of the existing charging standards are common in their geographic region, which EV manufacturers have sales or distribution in the area, and which charging standard those vehicles use. Adopting a charging standard that is used in nearby countries can ease EV travel between countries and increase the number of EV models available for purchase.
Communication and Interoperability
Having interoperable and open standards-based public EVSE infrastructure is critical to the success of the EV market
Communication and interoperability protocols allow EVSE to operate as a system and provide services to customers, making vehicle charging more accessible and convenient. Charging networks are businesses that remotely manage the operations and payment collection of numerous EVSE located at different sites. They do this by using EVSE that are connected to the internet or cellular service (via Wi-Fi or wired network). Once connected, EVSE can then offer cloud-based services that benefit the site host and customer (utilization monitoring, diverse payment options, app or web-based station locators, real-time status availability reports, and station usage reporting). In many countries, there exists multiple charging networks, encouraging competition, diversification, and increased EVSE deployment. In such cases, EV drivers will likely use different charging networks to charge their vehicle, which may require the driver to open multiple user accounts to pay for charging at each network they use. Alternately, if there are certain network interoperability communication protocols in place, an EV driver may have one user account that can be used to pay at different charging networks (i.e., analogous to network roaming with a mobile phone).
 By selecting EVSE with hardware that uses certain open standards-based communication and interoperability protocols, the EVSE can be easily switched to a different charging network without expensive equipment upgrades.
By selecting EVSE with hardware that uses certain open standards-based communication and interoperability protocols, the EVSE can be easily switched to a different charging network without expensive equipment upgrades.
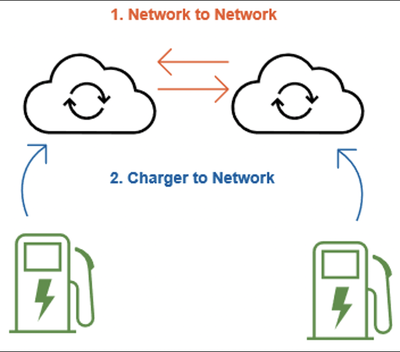
There are two main areas where interoperability protocols exist:
- Charger and Network Interoperability protocols allow EVSE owner-operators to switch charging networks without having to purchase a new EVSE or make expensive equipment upgrades.
- Network to Network Interoperability protocols allow drivers with a membership to one charging network to access other networks without having to become a member.