Data Collection and Management
Overview
Certain data about travel patterns, vehicle characteristics, electrical grid characteristics, vehicle populations, and the spatial arrangement of infrastructure can be critical when transitioning from traditional vehicles to electric vehicles (EVs). Some countries are already collecting robust datasets to guide this transition, while others may need to develop data collection methods as they embark on their journey toward electromobility.
Comprehensive travel pattern data, such as those provided by the National Household Travel Survey (NHTS) in the U.S., are particularly valuable for supporting national policy and investment decisions. The NHTS is one of the most comprehensive sources of travel data available, offering detailed insights into travel behaviors and patterns. Developing countries may not have access to the full range of data initially but can establish data collection systems to support their transition to EVs.
Typically collected datasets include:
- National: Household travel survey data (e.g., NHTS), vehicle stock, and usage data.
- State: Vehicle registration data, vehicle age, and emissions testing data.
- MPO (Metropolitan Planning Organizations): Origin-destination data, emissions testing, and traffic flow data.
- Private/ User: Telematics data, cell phone geolocation data, and GPS data.
Understanding these data types and their sources helps countries plan their transition to EVs more effectively and make informed decisions based on accurate, comprehensive information.
Figure 1. What is Travel Data? (K. Shankari and Abigail Wheelis, USAID).
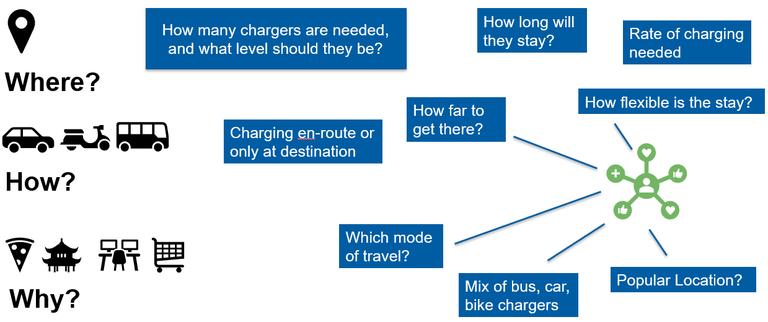
Fortunately, there are alternatives to traditional travel surveys that can be less time-consuming and resource-intensive. Data can be obtained from cell phone companies or aggregated from services like Inrix and Streetlight Data. However, this data can sometimes be costly or inaccessible in certain areas. Another viable option is to collect data through cell phone applications such as Waze or Near, or through apps specifically designed to enhance and electrify transportation systems.
Recently, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (NREL) Center of Integrated Mobility Sciences developed a versatile phone-app-based data collection tool, known as OpenPATH, which integrates data analysis capabilities. This customizable app, which can be adapted and translated for use in any country, is currently being used or considered in Lao People’s Democratic Republic (PDR), Mexico, and India. Additionally, other partners have chosen to deploy their own versions of OpenPATH in various countries. For example, it has been deployed by Fabrique des Mobilités Québec in Canada, the University of New South Wales in Australia, and Transway in Côte d'Ivoire, while the deployment in Kenya was in partnership with Harvard and the Busara Institute.
Unlike traditional static travel surveys, OpenPATH tracks and collects dynamic travel data, offering a transformative approach to data collection. Its flexibility allows for targeted use by specific populations or local priorities, with local authorities spearheading context-specific data collection and analysis. A notable feature of this tool is its ability to collect gender-disaggregated travel data, with detailed impacts discussed under the Gender-Mainstreaming Technical Theme.
Key Actions for Developing a Travel Data Collection Strategy
- Utilize Foundational Vehicle Data: Foundational data, such as transportation fuel use, vehicle stock, and vehicle kilometers traveled, provide insights into fleet transportation efficiency, emissions, and infrastructure needs. This data is critical for planning and improving transport systems and is discussed in more detail under the Planning a Fleet Transition Technical Theme.
- Travel Pattern Data: A significant challenge in achieving sustainable mobility is the lack of comprehensive data on travel habits. Traditional travel surveys gather detailed information on these habits. For example, the Federal Highway Administration’s (FHWA’s) Next Generation National Household Travel Survey (NextGen NHTS) Origin–Destination (OD) Data Products leverage in-vehicle and smartphone application-generated passive mobility data to provide national travel estimates. Moreover, tools like OpenPATH offer a more flexible, cost-efficient, and accessible method for data collection. OpenPATH enables resource-constrained transport agencies, cities, or any other local organization to collect high-quality data with minimal effort and cost, and to conduct robust data analyses without requiring extensive formal training. The collection of gender-disaggregated data, through the localized version of OpenPATH in Laos, demonstrates progress in making data collection tools more inclusive and context-specific.
- Leverage Specialized Data: Specialized data, including mode of travel, access to home charging, gasoline prices, electricity tariffs, drive cycle profiles, geospatial data, and electricity generation mix, helps identify the potential benefits of sustainable mobility and the best strategies for implementation. The phone app-based tool, OpenPATH, allows the user the input travel purpose as well as travel mode.
- Implement Geolocators: Geolocators and telematics can track vehicle movements and usage patterns, providing valuable data for optimizing transport systems and planning EV infrastructure. This is discussed in more detail in the Planning a Fleet Transition Technical Theme.
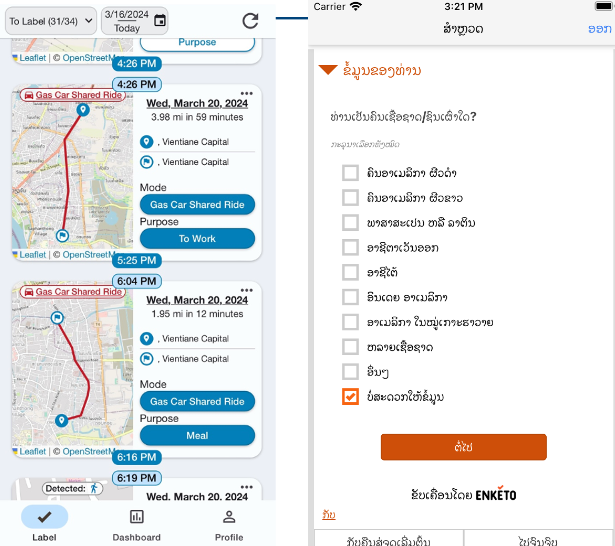
Country partners to the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) and NREL Partnership are keen on developing effective travel data collection and management strategies tailored to local priorities. Recently, the USAID-NREL Partnership customized OpenPATH for the Lao PDR, resulting in the development of “Laos OpenPATH,” which is currently collecting gender-disaggregated travel data to inform public charging infrastructure strategies for Vientiane Capital City. In this example, Lao PDR is evaluating the best locations for public EV charging stations, taking into consideration popular travel hubs and corridors, while also taking into consideration safety, lighting and ability for use by women and disabled people at the charging station.
Figure 2. Lao OpenPATH App with Samples From a Local Travel Diary (NREL OpenPATH).
Read more about USAID-NREL Partnership projects here and explore how we are driving innovative solutions in clean energy and sustainable transport.
Resources
How Do We Solve the Challenge of Data Interoperability in E-Mobility?
Ernst & Young and Eurelectric, 2024
This report explores the future digital EV ecosystem, emphasizing the need to unlock data and dismantle barriers to interoperability. It highlights the importance of standardization and regulation to ensure consistency and identifies how collaboration can release future value for all stakeholders.
Fleet Transition using Data Analytics
USAID-NREL Partnership, 2022
This lecture is one unit in a series presented in a 2021 virtual course, hosted by USAID and NREL Advanced Energy Partnership for Asia, on EV deployment fundamentals for Southeast Asia. This lecture covers protocols for prioritizing a fleet and designing a pilot to study to evaluate the project and understanding the varying needs of each fleet.
Building Blocks of Electric Vehicle Deployment: A Guide for Developing Countries
USAID-NREL Partnership, 2021
This report lays out a framework for policymakers, regulators, and other decision-makers in developing countries for how to plan, implement, and scale EV deployment in their jurisdictions. The “building blocks” of EV deployment address technical, institutional, or economic topics that together underpin a safe, sustainable, and efficient transition to an electrified transport sector. Data is highlighted as a critical building block, with a dedicated chapter focusing on its role in guiding effective EV deployment strategies.
Indicators for Sustainable Mobility
Institution for Transportation & Development Policy (ITDP), 2019
ITDP developed a series of indicators based on three categories: proximity to transit, access to opportunity, and city characteristics. This report defines criteria to evaluate mass transportation systems and then uses the criteria to assess 20 cities in the U.S. and compare the scores to those of eight cities in Canada and Mexico.
The Role of Open Data in Sustainable Transport
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ), 2015
This paper highlights how opening data can empower transport agencies to collect high-quality data efficiently and conduct robust analyses with minimal training. It emphasizes the benefits of open data for public transport improvements, including real-time service information and cost-effective data collection, while also addressing individual transport and environmental issues.
If you are interested in collaborating or learning more about the USAID-NREL Partnership's international sustainable transport and electric mobility initiatives, please contact us to learn more about partnership opportunities.

